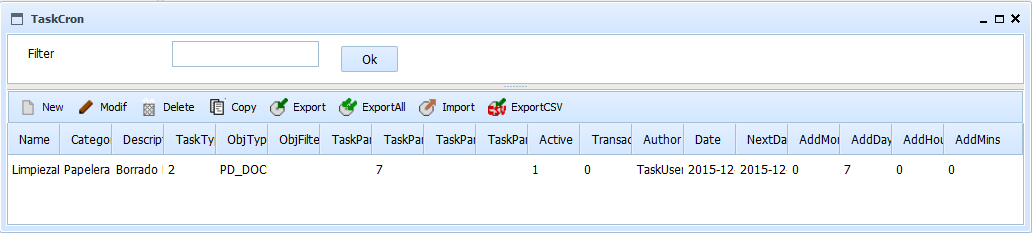
By selecting the option to manage Scheduled Tasks, will appear the form "list of Scheduled Tasks". This form allows you to maintain and define the Scheduled Tasks.
OPD includes the possibility of defining scheduled tasks to perform various maintenance and integration tasks.
There is no limit to the number of tasks that can be defined, but must be considered the execution time of each of them, because if too many or too complex tasks are defined, it may happen that some had not finished when it should begin again with them. If necessary, the system can be configured so that different groups of tasks run on different computers, allowing the work to be parallelized and to scale the system. Each task has an attribute named "category", which allows to group them, so that each computer can run all scheduled tasks in a particular category. It should be noted that also a computer alone can run all tasks of any category.
You can define different tasks of the same type but with different parameters (eg you can program the export of a folder structure / records with a frequency and the export of another structure with another frequency and destinations).
For each defined task, in addition to the specific parameters of the task kind, it is indicated the execution frequency and date-time of the next run . That way, it can be programmed, for example every 7 days, starting from Saturday at 23:00, or every hour, beginning at 9:00.
The task execution involves two steps. When the day and time of execution of a task is reached, a "work order" of the task (a "photocopy" of the task) is generated by the computer in charge of generating the task category (or all) . That "work order" in turn is queued and will be executed when the computer (s) responsible of the execution of the tasks ends the previous tasks.
So the order is created at the right time and with the right parameters, but can be run with a slight delay. Even if by some sort of incident, I could not get to run at the time, the "work order" is recorded to be pending. When the component responsible for executing tasks becomes active, it will process all the pending work orders.
The list of pending task can be reviewed in List of pending task and the list of ended tasks in List of ended tasks. It is the responsibility of the administrator to delete the information from the completed tasks to prevent excessive growth of database tables and reduce performance..
The system has big scalability. In a small system, one computer can generate and run all the tasks; in a big system, 1 or 2 computers can generate the "work orders" from the task and several computers run the generated "work orders", each one "specialized" in a category.
It's possible to define the tasks as transactional.That is, the task will be executed over all the affected objects (i.e.: all the documents in a folder) and if any one fails, the operation is canceled for all the objects, so the system maintains the coherence. If the task is not transactional, the operation is performed on some objects and may fail in others.
Tasks can be turned on and off, so that they can be fully defined and tested but not executed until needed. They can again be turned off when required. Activation controls the generation of the "work order", ie if a task is off, no "work orders" are generated.
To enable the generation of scheduled tasks and task execution (programs or associated events) must edit the configuration file Prodoc.properties of the computers on which it is intended to build or run tasks. The available parameters are:To enable the generation of scheduled tasks and execution of tasks (schedulled or associated to events), you must edit the configuration file Prodoc.properties of the computers on which it is intended to generate or run tasks. The available parameters are:
It must be carefully adjusted the distribution of tasks. If multiple computers are assigned all tasks (or the same type) and the sampling frequency is high, they can run the same task simultaneously, doubling the result or failing. If you assign the same task to several computers, the sampling times should be very different and be spaced. In the simplest case it can be a single computer for execution of all tasks, or one for each category of task.
Similarly, it should be carefully adjusted the sampling frequency. When sampling a lot, the execution will conform to the exact programed minute or second but the system is overloaded. Unless it is essential, it is better to sample with low frequency, although you risk delaying to running of the task a few minutes.
To filter the Task or list of Tasks you want to review, just enter part of the name in the text box and press "ok". The list of Tasks that meet the conditions will be shown on the results table. Pressing the button without entering any value you see all the elements on which the user has permission. The results table shows the data:

This results table can be sorted by selecting the header of each column. You can also change the size of each column by dragging the separator line in the headers.
Above the table of results there are several buttons for performing operations on the selected item. The available operations are:
 Add a new element
Add a new element Delete the selected element (if it is not used in some document or folder)
Delete the selected element (if it is not used in some document or folder) Modify the selected element
Modify the selected element Create a new item as a copy of the selected item
Create a new item as a copy of the selected item Export the selected item
Export the selected item Export all items listed
Export all items listed Import from file one or more previously saved items
Import from file one or more previously saved items Export all items listed in CSV format so it can be imported in Databases or Spreadsheet
Export all items listed in CSV format so it can be imported in Databases or SpreadsheetIt should be noted on export and import, that some elements may have dependency on others, so you must export all related and imported at the time of it in the proper order.
In the event of an error (lack of user permissions, data inconsistency, etc.), the operation is canceled and will present the reason for the error to the user.
View Scheduled Tasks Maintenance, Panding Tasks List y Ended Tasks List